
Daisy, a caring and dedicated Border Collie, has cared for Max and Bella since they were puppies. They were not her biological children, but she adopted them as her own. They developed an unbreakable bond, creating a family unit defined by love, not blood.
Daisy was getting older, and her quick steps were fading. Her loyal companions, Max, an elderly golden retriever, and Bella, an energetic beagle, cared for her as she had done for them all their lives. They felt her pain, her declining health, and her weakness.

Daisy’s illness worsens, and Max and Bella become her caregivers. They would caress her, provide comfort with gentle licks, and stay by her side all day and night. The roles have been reversed, and they seem to have realized that it is their turn to care for their sick mother.
Max, with his deep, loving eyes, slept close to Daisy, his presence bringing comfort. Bella, who was usually full of energy, took it upon herself to be Daisy’s fun distraction, bringing some joy to her otherwise terrible days.
Daisy realized her time was running out one sunny afternoon as she slept in her favorite spot in the garden, surrounded by the flowers she loved. Max and Bella noticed the gravity in the air, anticipating the big change that was about to happen.

Max and Bella approached Daisy gently, one on each side. They laid their heads on her, as if they were silently pledging to be there for her until the end. Daisy stared at them, her eyes filled with gratitude and love for her loyal friends.
Daisy walked away quietly as the sun fell below the horizon, sending a warm orange glow across the grass. Her sweethearts Max and Bella were present, comforting her as she crossed the Rainbow Bridge.
Max and Bella’s eyes filled with tears as they looked at their dead mother. They were lost from their Lord, who protected them and loved them like her own. However, the love they felt for Daisy and the love she gave them will live in their hearts forever.

In the days that followed, Max and Bella found comfort in each other’s company. Their friendship, formed from their shared love for Daisy, grows stronger. They often sat together in the garden, surrounded by Daisy’s favorite flowers, as if sharing fond memories of their mother.
Max and Bella’s sad farewell to their ill mother, Daisy, is an example of the extraordinary relationships that can be built between dogs and their adopted family members.

In a world where love knows no bounds, Max and Bella show that a dog’s love and commitment to their adoptive family is as deep and unbreakable as any other dog.
Their narrative serves as a reminder of the beauty of love and the lasting connections that make life more meaningful.
Can dogs really detect Covid-19 infections faster and more accurately than a lateral flow test?
Results indicated that not only can dogs detect Covid faster, but they can also do so in a non-intrusive manner – so no need to swab your throat or nose
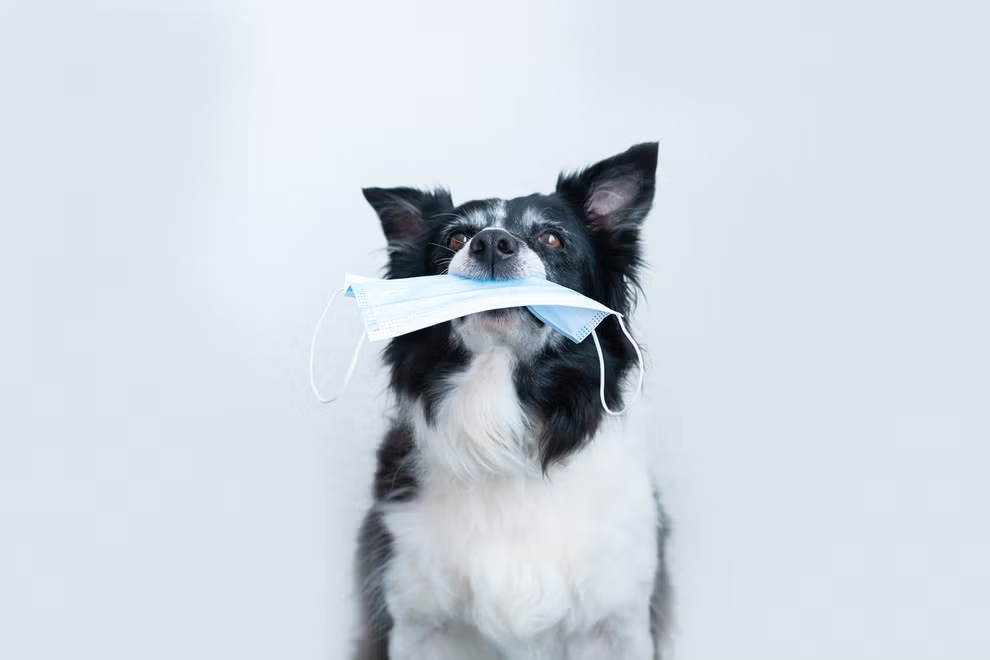

Dogs can detect Covid-19 faster and more accurately than a PCR test, a new study shows.
Researchers looked at the ability of canines to recognise the virus and its variants, even when they are obscured by other viruses, like those from common colds and flu.
More than 400 scientists from over 30 countries contributed to the study as well as 147 scent dogs, according to the findings published in the Journal of Osteopathic Medicine.
After analysing many studies covering both field and clinical experiments, Professor Dickey and Junqueira found that dogs who are trained to sniff out scents are “as effective and often more effective” than antigen tests.
A total of 53 dogs were trained to sniff out Covid scents, while 37 were not and scientists found that the dogs that were not trained were in some cases “slightly superior” to those that were pre-trained.
“The previously untrained dogs have the advantage that they are not as prone to indicating on scents other than the Covid–19 associated scent,” the paper said.
The results indicated that not only can dogs detect Covid faster, but they can also do so in a non-intrusive manner. This means you won’t need to put a swab in your throat or nose.
How can dogs detect the virus?
This essentially comes down to the dog’s highly evolved nose with its ability to sense out smells quicker.
Dogs possess up to 300 million olfactory receptors in their noses, compared to about six million in humans. And the part of a dog’s brain that is devoted to analysing smells is about “40 times greater” than humans. Canines also have ‘neophilia’, which means they are attracted to new and interesting odours
And so, with all these enhancements, dogs can detect very low concentrations of odours associated with Covid infections.
“They can detect the equivalent of one drop of an odorous substance in 10.5 Olympic-sized swimming pools,” Professor Dickey said. “For perspective, this is about three orders of magnitude better than with scientific instrumentation.”
Scientists also found that in some cases, the animals were also able to detect the virus in pre-symptomatic and asymptomatic patients, “whose viral load was too low for conventional tests to work.”
Professor Dickey has said that dogs can also differentiate Covid and its different variants in the presence of other respiratory viruses. This included the common cold or flu.
“They’re much more effective. In fact, one of the authors that we quote in the paper commented that the RT-PCR test is not the gold standard anymore. It’s the dog. And they’re so quick,” he added. “They can give you the yes or no within seconds if they’re directly smelling you.”
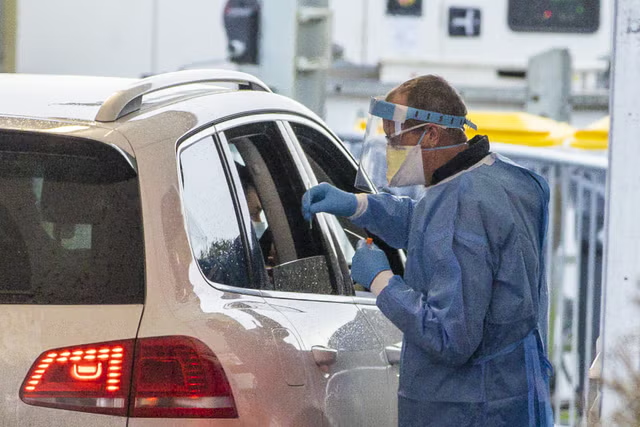

How was the study conducted to see if dogs can really detect Covid-19?
In some studies, the dogs gave a person a quick sniff, sitting down to see if the person has Covid. In another study, the dog was given a sweat sample to smell for a few minutes.
The press release has said that scent dogs, such as beagles, basset hounds and coonhounds are the ideal candidates for sniffing out the virus, given their “natural tendencies to rely on odours to relate to the world.”
But the studies which the researchers analysed showed a variety of dogs were up for the challenge and were able to sniff out the Covid odour. With a few weeks of training, puppies, older dogs, purebred and mixed breeds, both male and female were able to sniff such odours out and “all performed admirably,” the Eureka Alert press release said.
Although there has been success with dogs detecting such viruses, researchers believe there are still many challenges with using dogs for medical diagnoses.
“There’s quite a bit of research, but it’s still considered by many as a kind of a curiosity,” said Professor Dickey.
In conclusion, Professor Dickey and Junqueira said after reviewing the studies, believe that scent dogs deserve “their place as a serious diagnostic methodology that could be particularly useful during future pandemics, potentially as part of rapid routine health screenings in public spaces.”
“Perhaps, most importantly, we argue that the impressive international quality and quantity of COVID scent dog research described in our paper for the first time, demonstrates that medical scent dogs are finally ready for a host of mainstream medical applications,” they added.


Leave a Reply