There are many possible causes for white tongue, and in some cases, it comes with an unpleasant odor and mouth dryness. To get rid of it, sometimes you just need to brush your teeth. But what should you do if that doesn’t help?

What white tongue is
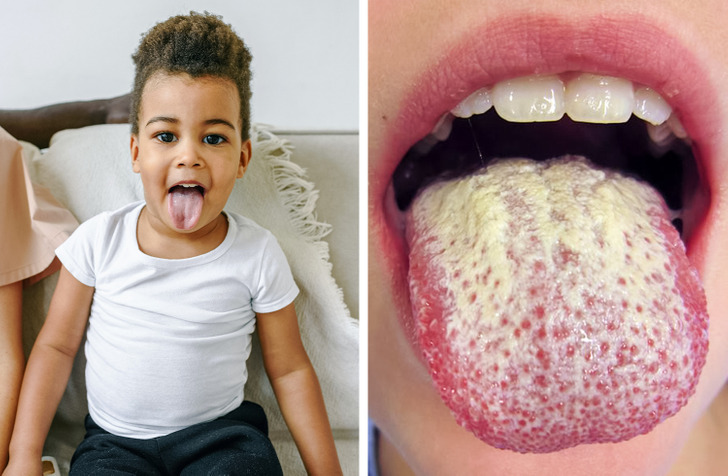
The white film may cover the entire tongue, part of it, or appear as spots. At the same time, an unpleasant odor and taste in the mouth may appear. It looks as if there are small white hairs on the tongue’s surface. In fact, they are buds covered with organic particles, bacteria, and dead cells.
White plaque on the tongue (which can also be yellow) may appear for different reasons, like due to irritation or because of an infection. It usually disappears after several days. If the situation doesn’t change for several weeks, and it’s painful to eat and talk, it’s best to see a doctor.
It’s important to note that the plaque may not only be white. While a pink tongue is normal, a brown tongue means the person drinks too much coffee or tea. A yellow tongue means there’s something wrong with the liver, and a red tongue is a sign that the person lacks vitamin B.
Why the tongue becomes white
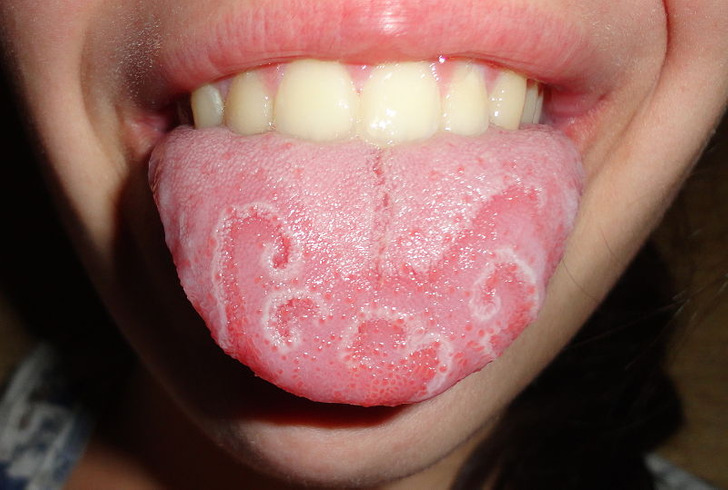
Usually, the tongue becomes white due to bacteria, leftover bits of food, or dead cells that get stuck in between the buds. Because of this, the buds may increase in size or become inflamed. This is how white spots on the tongue’s surface appear.
Sometimes, the plaque appears due to an illness. For example, the geographic tongue is also a condition where white spots appear on the tongue. It’s quite rare, and the causes are unknown, but the condition itself is often connected to eating foods that irritate the tongue. It may also be a reaction to stress, an illness, or hormonal changes.
Why white plaque appears on the tongue
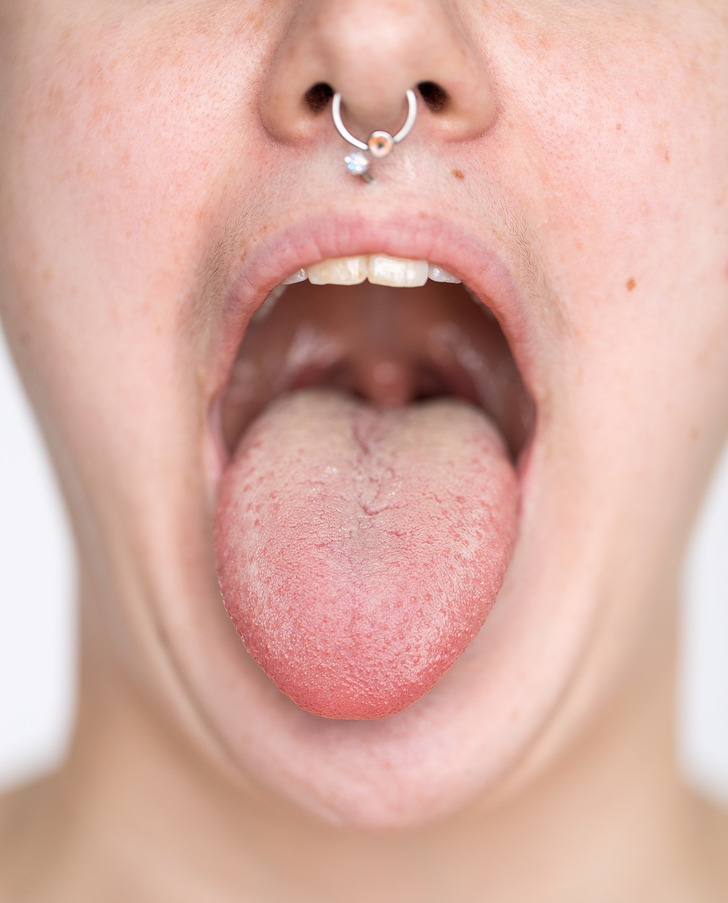

There are some things that make the appearance of white plaque on the tongue more probable:
- Age
- Taking antibiotics (white-yellow plaque appearing when there’s a fungal infection in the mouth)
- A diet that’s lacking enough fruits, vegetables, vitamin B12, and iron
- A weak immune system
- Bad mouth hygiene
- Dental prosthetics or other objects that can damage the tongue
- Dehydration and mouth dryness
What piercings have to do with white tongue
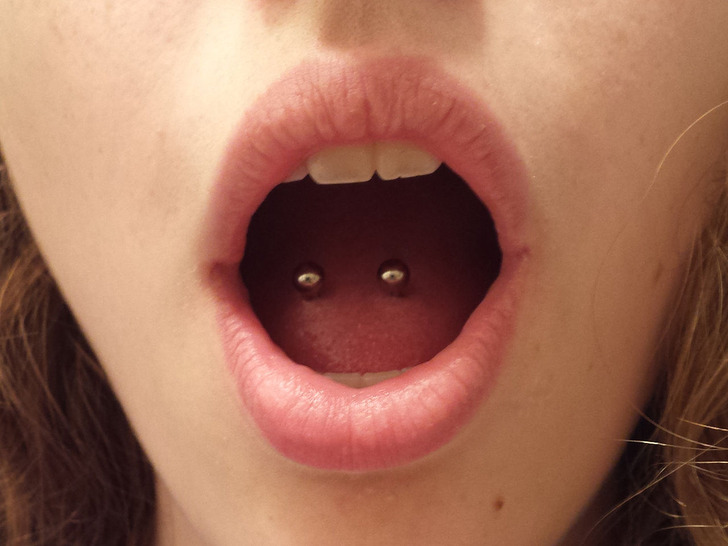
Right after piercing the tongue, there might be some white film present. This happens because the number of bacteria on the tongue increases, and it’s normal. Antibacterial mouthwash will help you get rid of it. Plus, there might be a ring around the piercings, which is normal too, and it means the tissue is healing.
If the plaque appears due to an injury (including piercings), the healing should take around 1.5 weeks. You should avoid irritants, such as hot, spicy, or sour foods and drinks.
How to get rid of white tongue at home
- Practice good mouth hygiene.
- Drink enough water.
- Brush your teeth using a soft toothbrush.
- Use a mild fluoride toothpaste — one that doesn’t contain sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Use fluoride mouthwash.
- Brush your tongue or use a tongue scraper to remove the white coating.
- Drink cold drinks through a straw.
- Avoid food and drinks that are spicy, salty, acidic, or very hot in temperature.
Who to talk to if you’re worried about your white tongue
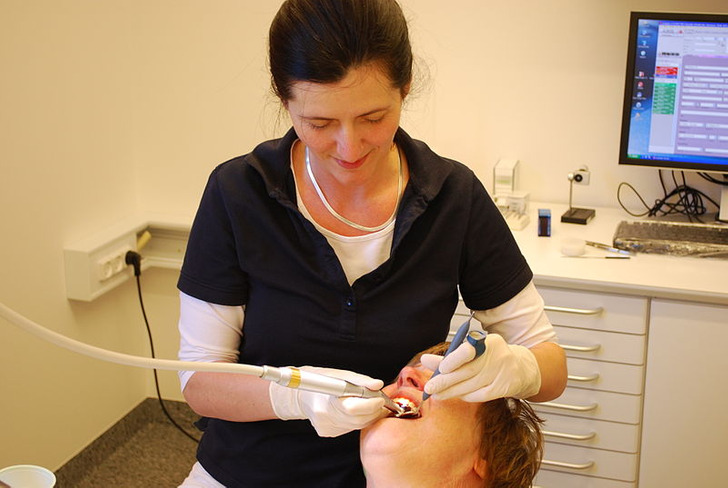
- Your dentist can help you remove the white film from the tongue and prescribe medications if needed.
- Your GP can diagnose the tongue, prescribe you certain medications and determine if the white tongue is an indicator of a more serious issue.
What do you do about white tongue?
Preview photo credit Genusfotografen (genusfotografen.se) & Wikimedia Sverige (wikimedia.se) / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0, Martanopue / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 3.0
An “unusual” dog called Pig that has no neck and a body that appears to have been chopped in half has become an internet sensation.

More than 27,000 people have joined a fans’ group in honour of the strange-looking animal, who is quickly becoming one of Alabama’s biggest stars.
Pig, who bears little resemblance to the curly-tailed farmyard animal, suffers from short spine syndrome and has bones that are fused together.
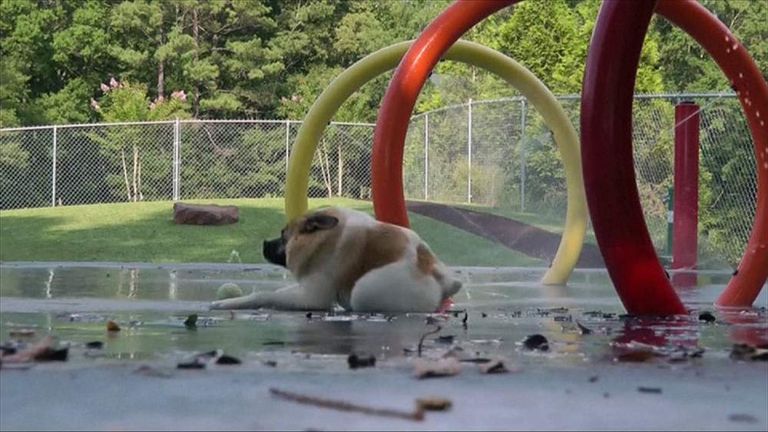

Her condition causes her to walk like a gorilla and she often loses her balance, toppling over like a toddler.
But she is not letting her disability get her down and her adventures are chronicled on a Facebook page called Pig the Unusual Dog.
Kim Dillenbeck, who adopted Pig after finding her in a forest, said her pet is “living life to the fullest”.
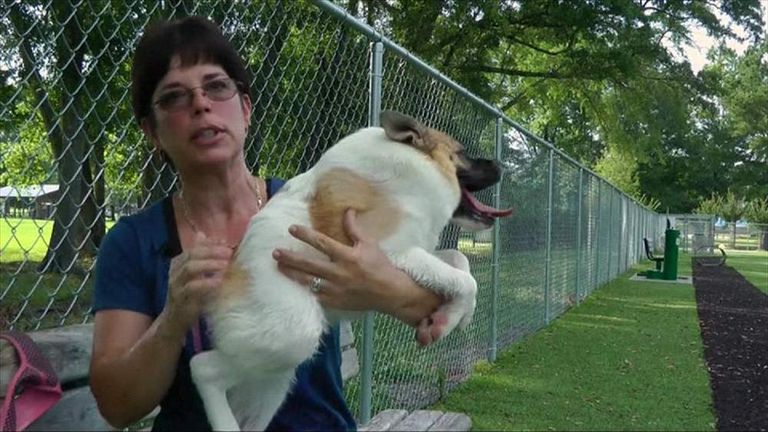

“She’s missing several inches of her spine (and) her joints, her hips … none of them are in the right position,” she added.
Dr Rachael Hudson-Breland, the vet who treats Pig, said the eight-month-old mutt is given “rock star” treatment at her clinic.
“I don’t think Pig really knows she looks different,” she said.
“She runs around, she plays. The only thing with Pig is … she has respiratory issues, so when she’s running around she gets a little more tired than most dogs.”



Leave a Reply